1. AVERAGE
The AVERAGE function should remind you of simple averages of data such as the average number of shareholders in a given shareholding pool.=AVERAGE(number1, [number2], …)
Example:
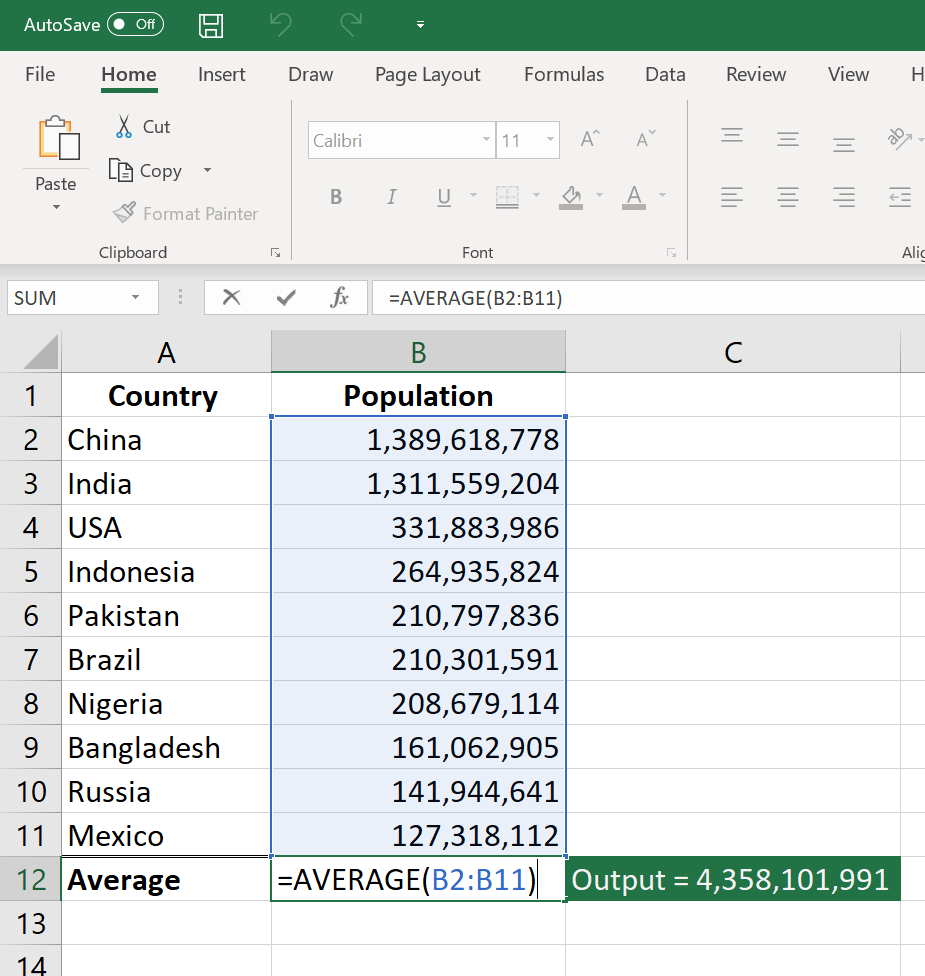
=AVERAGE(B2:B11) – Shows a simple average, also similar to (SUM(B2: B11)/10)
2. COUNT
The COUNT function counts all cells in a given range that contains only numeric values.=COUNT(value1, [value2], …)
Example:
COUNT(A:A) – Counts all values that are numerical in A column. However, you must adjust the range inside the formula to count rows.
COUNT(A1:C1) – Now it can count rows.
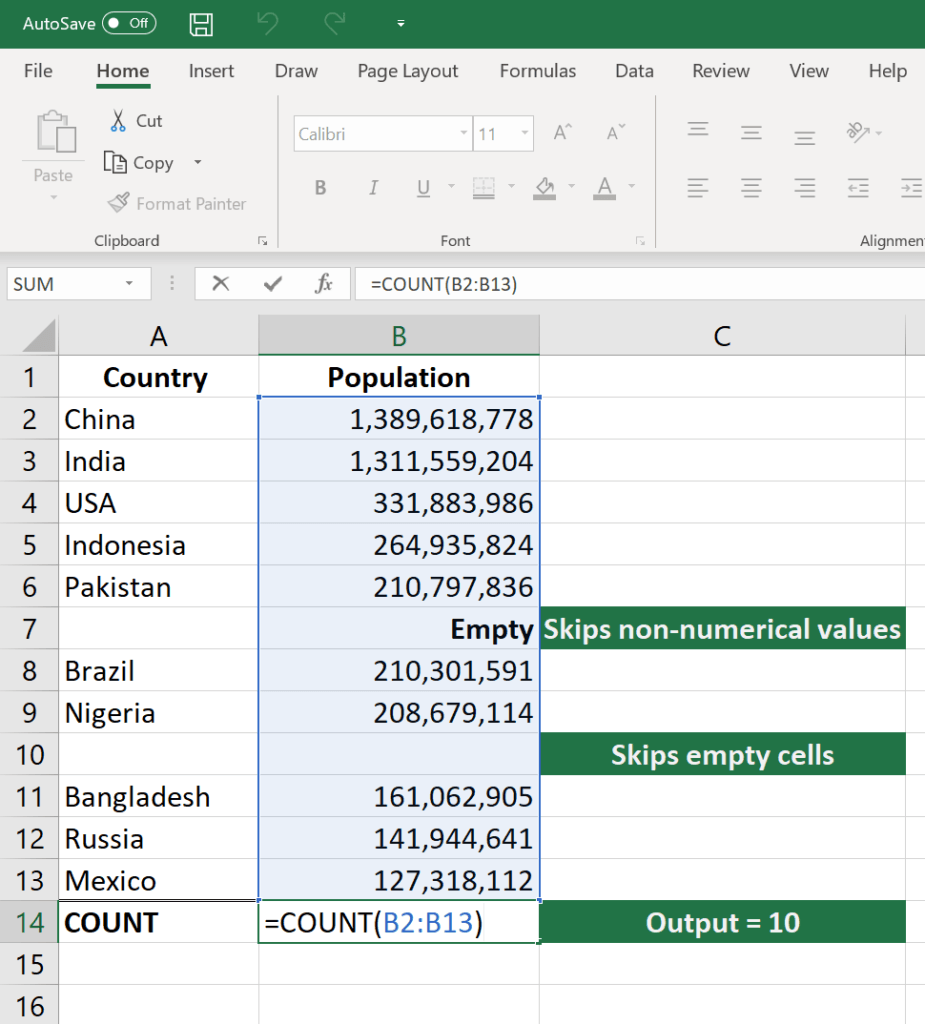
Image: CFI’s Excel Courses.
3. COUNTA
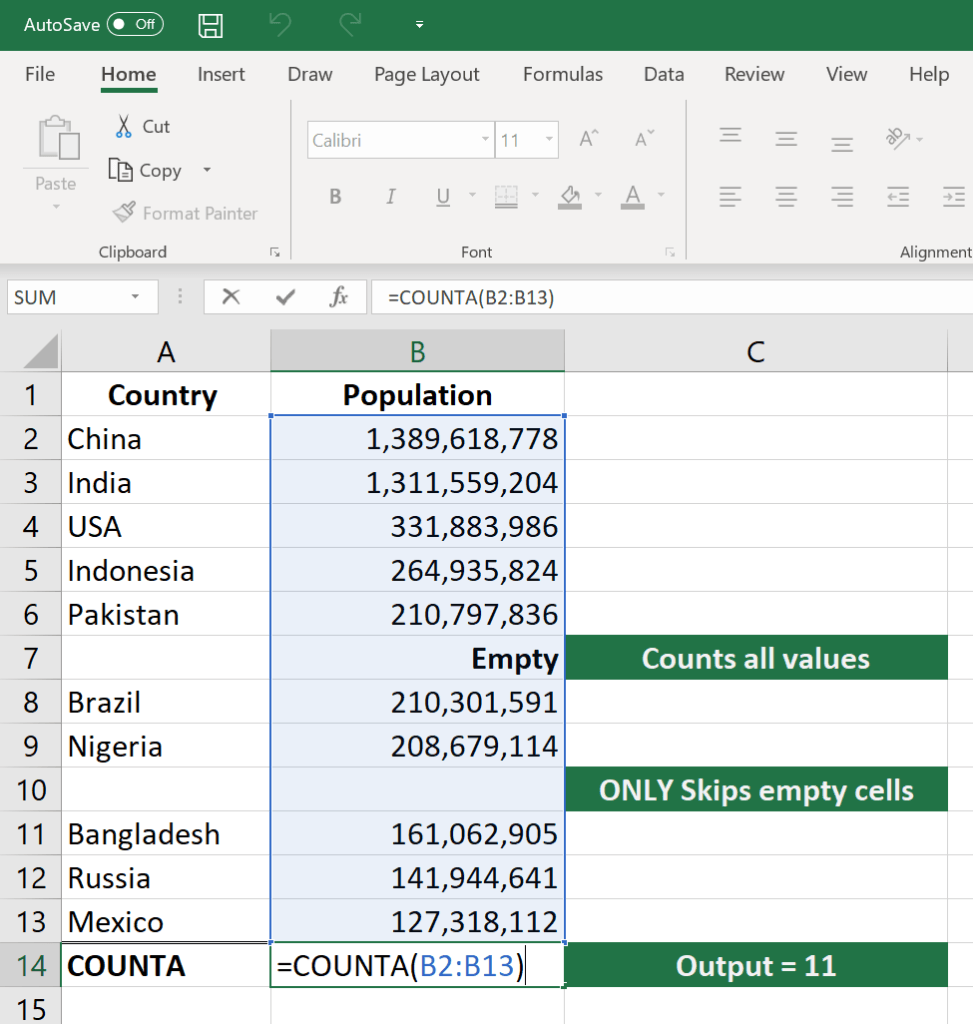
Like the COUNT function, COUNTA counts all cells in a given rage. However, it counts all cells regardless of type. That is, unlike COUNT that relies on only numerics, it also counts dates, times, strings, logical values, errors, empty string, or text.=COUNTA(value1, [value2], …)
Example:
COUNTA(C2:C13) – Counts rows 2 to 13 in column C regardless of type. However, like COUNT, you can’t use the same formula to count rows. You must make an adjustment to the selection inside the brackets for example COUNTA(C2:H2) will count columns C to H


No comments:
Post a Comment