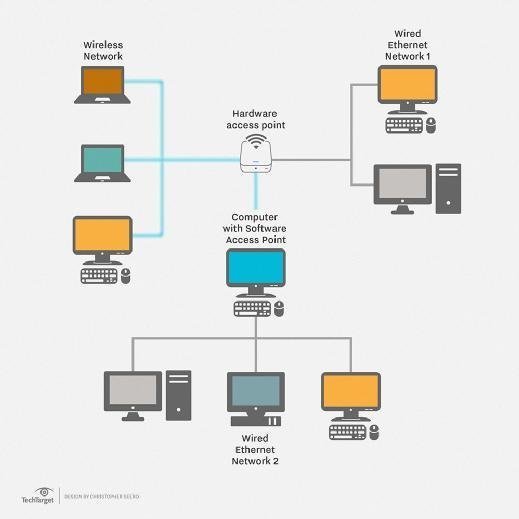
Local Area Network
(LAN)
A local area network (LAN)
is a group of computers and associated devices that share a common
communications line or wireless link to a server. Typically, a LAN encompasses
computers and peripherals connected to a server within a distinct geographic
area such as an office or a commercial establishment. Computers and other
mobile devices use a LAN connection to share resources such as a printer or
network storage.
A local area network may serve
as few as two or three users (for example, in a small-office network) or
several hundred users in a larger office. LAN networking comprises cables,
switches, routers and other components that let users connect to internal
servers, websites and other LANs via
Ethernet
and Wi-Fi are the two primary ways to enable LAN connections. Ethernet is a
specification that enables computers to communicate with each other. Wi-Fi uses
radio waves to connect computers to the LAN. Other LAN technologies, including Token
Ring, Fiber Distributed Data Interface and ARCNET, have
lost favor as Ethernet and Wi-Fi speeds have increased. The rise of
virtualization has fueled the development of virtual LANs, which allows
network administrators to logically group network nodes and partition their
networks without the need for major infrastructure changes.Typically, a suite
of application programs can be kept on the LAN server. Users who need an
application frequently can download it once and then run it from their local
device. Users can order printing and other services as needed through
applications run on the LAN server. A user can share files with others stored
on the LAN server; read and write access is maintained by a network
administrator. A LAN server may also be used as a web server if
safeguards are taken to secure internal applications and data from outside
access.


No comments:
Post a Comment