Internal Computer Hardware
Computer Hardware is the physical part of a computer, as
distinguished from the computer software that executes or runs on the
hardware. The hardware of a computer is infrequently changed, while software
and data are modified frequently. The term soft refers to readily created,
modified, or erased. These are unlike the physical components within the
computer which are hard.
When you think of the term computer hardware you probably think
of the guts inside your personal computer at home or the one in your classroom.
However, computer hardware does not specifically refer to personal computers.
Instead, it is all types of computer systems. Computer hardware is in embedded
systems in automobiles, microwave ovens, CD players, DVD players, and many more
devices. In 2003, only 0.2% of all microprocessors sold were for personal
computers. How many other things in your house or your classroom use computer
hardware?
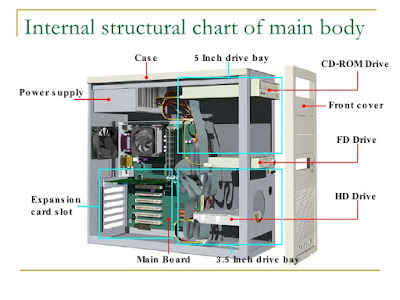
Inside Computer
Motherboard
The motherboard is the body or mainframe of the computer,
through which all other components interface. It is the central circuit board
making up a complex electronic system. A motherboard provides the electrical
connections by which the other components of the system communicate. The mother
board includes many components such as: central processing unit (CPU), random
access memory (RAM), firmware, and internal and external buses.
Motherboard
Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit (CPU; sometimes just called
processor) is a machine that can execute computer programs. It is sometimes
referred to as the brain of the computer.
CPU Diagram
There are four steps that nearly all CPUs use in their
operation: fetch, decode, execute, and writeback. The first step, fetch,
involves retrieving an instruction from program memory. In the decode step, the
instruction is broken up into parts that have significance to other portions of
the CPU. During the execute step various portions of the CPU, such as the
arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and the floating point unit (FPU) are connected so
they can perform the desired operation. The final step, writeback, simply
writes back the results of the execute step to some form of memory.
Random Access Memory
Random access memory (RAM) is fast-access memory that is cleared
when the computer is power-down. RAM attaches directly to the motherboard, and
is used to store programs that are currently running. RAM is a set of
integrated circuits that allow the stored data to be accessed in any order (why
it is called random). There are many different types of RAM. Distinctions
between these different types include: writable vs. read-only, static vs.
dynamic, volatile vs. non-volatile, etc.
RAM
Firmware
Firmware is loaded from the Read only memory (ROM) run from the
Basic Input-Output System (BIOS). It is a computer program that is embedded in
a hardware device, for example a microcontroller. As it name suggests, firmware
is somewhere between hardware and software. Like software, it is a computer
program which is executed by a microprocessor or a microcontroller. But it is
also tightly linked to a piece of hardware, and has little meaning outside of
it. Most devices attached to modern systems are special-purpose computers in
their own right, running their own software. Some of these devices store that
software (“firmware”) in a ROM within the device itself
Power Supply
The power supply as its name might suggest is the device that
supplies power to all the components in the computer. Its case holds a
transformer, voltage control, and (usually) a cooling fan. The power supply
converts about 100-120 volts of AC power to low-voltage DC power for the
internal components to use. The most common computer power supplies are built
to conform with the ATX form factor. This enables different power supplies to
be interchangable with different components inside the computer. ATX power
supplies also are designed to turn on and off using a signal from the
motherboard, and provide support for modern functions such as standby mode.
Removable Media Devices
If your putting something in your computer and taking it out is
most likely a form of removable media. There are many different removable media
devices. The most popular are probably CD and DVD drives which almost every
computer these days has at least one of. There are some new disc drives such as
Blu-ray which can hold a much larger amount of information then normal CDs or
DVDs. One type of removable media which is becoming less popular is floppy
disk.
CD
CDs are the most common type of removable media. They are
inexpensive but also have short life-span. There are a few different kinds of
CDs. CD-ROM which stands for Compact Disc read-only memory are popularly used
to distribute computer software although any type of data can be stored on
them. CD-R is another variation which can only be written to once but can be
read many times. CD-RW (rewritable) can be written to more than once as well as
read more than once. Some other types of CDs which are not as popular include
Super Audio CD (SACD), Video Compact Discs (VCD), Super Video Compact Discs
(SVCD), PhotoCD, PictureCD, CD-i, and Enhanced CD.
CD-ROM Drive
There are two types of devices in a computer that use CDs: CD-ROM
drive and a CD writer. The CD-ROM drive used for reading a CD. The CD writer
drive can read and write a CD. CD writers are much more popular are new
computers than a CD-ROM drive. Both kinds of CD drives are called optical disc
drives because the use a laser light or electromagnetic waves to read or write
data to or from a CD.
DVD
DVDs (digital versatile discs) are another popular optical disc
storage media format. The main uses for DVDs are video and data storage. Most
DVDs are of the same dimensions as compact discs. Just like CDs there are many
different variations. DVD-ROM has data which can only be read and not written.
DVD-R and DVD+R can be written once and then function as a DVD-ROM. DVD-RAM,
DVD-RW, or DVD+RW hold data that can be erased and re-written multiple times.
DVD-Video and DVD-Audio discs respectively refer to properly formatted and
structured video and audio content. The devices that use DVDs are very similar
to the devices that use CDs. There is a DVD-ROM drive as well as a DVD writer
that work the same way as a CD-ROM drive and CD writer. There is also a DVD-RAM
drive that reads and writes to the DVD-RAM variation of DVD.
DVD
Blu-ray
Blu-ray is a newer optical disc storage media format. Its main
uses are high-definition video and data storage. The disc has the same
dimensions as a CD or DVD. The term “Blu-ray” comes from the blue laser used to
read and write to the disc. The Blu-ray discs can store much more data then CDs
or DVDs. A dual layer Blu-ray disc can store up to 50GB, almost six times
thecapacity of a dual layer DVD (WOW!). Blu-ray discs have similar devices used
to read them and write to them as CDs have. A BD-ROM drive can only read a
Blu-ray disc and a BD writer can read and write a Blu-ray disc.
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk is a type of data storage that is composed of a
disk of thin, flexible(“floppy”) magnetic storage medium encased in a square or
rectangular plastic shell. Floppy disks are read and written by a floppy disk
drive. Floppy disks are a dying and being replaced by the optical and flash
drives. Many new computers do not come with floppy drives anymore but there are
a lot of older ones with floppy drives lying around. While floppy disks are
very cheap the amount of storage on them compared to the amount of storage for
the price of flash drives makes floppy disks unreasonable to use.
Floppy Disk
Internal Storage
Internal storage is hardware that keeps data inside the computer
for later use and remains persistent even when the computer has no power. There
are a few different types of internal storage. Hard disks are the most popular
type of internal storage. Solid-state drives have grown in popularity slowly. A
disk array controller is popular when you need more storage then a single har
disk can hold.
Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD) is a non-volatile storage device which
stores digitally encoded data on rapidly rotating platters with magnetic
surfaces. Just about every new computer comes with a hard disk these days
unless it comes with a new solid-state drive. Typical desktop hard disk drives
store between 120 and 400GB, rotate at 7,200 rpm, and have a madia transfer
rate of 1 Gbit/s or higher. Hard disk drives are accessed over one of a number
of bus types, including parallel ATA(also called IDE), Serial ATA (SATA), SCSI,
Serial Attached SCSI, and Fibre Channel.
Hard Drive
Solid-State Drive
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a data storage device that uses
solid-state memory to store persistent data. An SSD emulates a hard disk drive,
thus easily replacing it in any application. SSDs have begun to appear in
laptops because they can be smaller than HDDs. SSDs are currently more
expensive per unit of capacity than HDDs which is why they have not caught on
so quickly.
Disk Array Controller
A disk array controller is a device which manage the physical
disk drives and presents them to the computer as logical units. It almost
always implements hardware RAID. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Drives)
is a technology that employs the simultaneous use of two or more hard disk
drives to achieve greater levels of performance, reliability, and/or larger
data volume sizes. A disk array controller also provides additional disk cache.



No comments:
Post a Comment